Ran Ju, Ling Ge, Wenjing Geng, Tongwei Ren, and Gangshan Wu

Figure 1. Saliency detection aims at finding the most conspicuous regions rapidly from sight. We demonstrate that depth cue contributes a powerful impact in visual attention. First row: color image (left view), disparity map and saliency map generated by our method. Second row: saliency results generated by three depth based methods. Third row: results generated by three color based methods.
Most previous works on saliency detection are dedicated to 2D images. Recently it has been shown that 3D visual information supplies a powerful cue for saliency analysis. In this paper, we propose a novel saliency method that works on depth images based on anisotropic center-surround difference. Instead of depending on absolute depth, we measure the saliency of a point by how much it outstands from surroundings, which takes the global depth structure into consideration. Besides, two common priors based on depth and location are used for refinement. The proposed method works within a complexity of O(N) and the evaluation on a dataset of over 1000 stereo images shows that our method outperforms state-of-the-art.
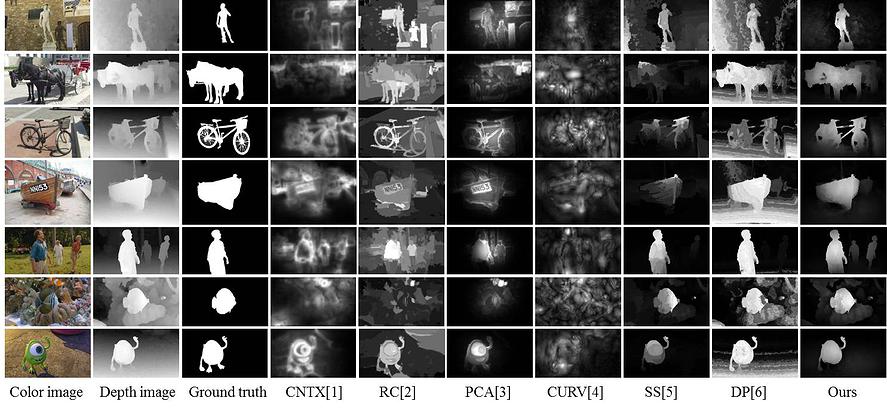
Figure 2. Comparisons with state-of-the-art methods. The first column shows the left views of the stereo images. The second and third column shows the depth images and ground truth salient object masks repectively. The next three columns are the saliency results of color image based methods. The last four columns show the results of depth saliency methods.
Please cite our paper if you use our dataset or code.